what is the blockchain
Since the invention of Bitcoin in 2008, blockchain technology has experienced a remarkable progress. Between 2012 and 2024, blockchain has evolved from a specialized technology that underpinned cryptocurrencies to a key component of worldwide digital innovation. Along the way, there have been significant developments in alternative cryptocurrency markets, smart contract introductions with Ethereum, and the proliferation of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) and decentralized finance (DeFi). As blockchain was adopted by sectors across the globe, it encountered difficulties like regulatory scrutiny and scalability. Blockchain is currently leading the way in new developments like Web3 and the metaverse, indicating its crucial role in determining how the digital world will develop in the future.
blockchain development from 2008 to 2024:
Since the invention of Bitcoin in 2008, blockchain technology has seen substantial development. In its early years (2008–2012), blockchain was intended to serve as the foundation for Bitcoin
1. The Birth of Blockchain: Bitcoin’s Genesis (2008-2010)
The development of Bitcoin is closely linked to the emergence of blockchain technology. Under the alias Satoshi Nakamoto, a person or group released a whitepaper titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System” in 2008. The idea behind Bitcoin, a decentralized digital money that would function without the need for a bank or other central authority, was described in this document.
The blockchain, a distributed ledger system that logged every transaction across a network of computers (nodes), was the fundamental component of Bitcoin. Transparency, security, and immutability were all guaranteed by the blockchain, which prevented transactions from being removed or changed once they were added. This breakthrough made digital currency transactions peer-to-peer and trustless by resolving the double-spending issue.

Bitcoin’s Early Adoption and Growth (2010-2012)
The initial years of Bitcoin, spanning from 2010 to 2012, were pivotal in laying the groundwork for the eventual development of a worldwide digital currency. During this time, Bitcoin evolved from an experimental idea that a small number of enthusiasts for cryptography embraced to a burgeoning digital currency with a devoted user base.
The first major milestone for Bitcoin was reached in 2010 when BitcoinMarket.com, the first cryptocurrency exchange, opened for business, enabling users to swap Bitcoin for fiat money. This innovation gave individuals a concrete method to give the virtual money a value, which was crucial to the early acceptance of Bitcoin. At the same time, as more individuals got interested in the technology, the value of Bitcoin started to slowly increase.
The renowned Pizza Bitcoin

The Rise of Alternative Cryptocurrencies (2012-2014)
The emergence of alternative cryptocurrencies, sometimes known as “altcoins,” between 2012 and 2014 really started to diversify the cryptocurrency ecosystem. The potential of blockchain technology was increased by these new cryptocurrencies, even if Bitcoin had already cemented its position as the leader of digital currencies with a number of innovative features and ideas.
Charlie Lee, a former Google programmer, introduced Litecoin in 2011, making it one of the first and most notable altcoins. Because of its quicker transaction times and use of a different hashing algorithm (Scrypt), Litecoin was intended to be the “silver to Bitcoin’s gold,” making mining more accessible to regular users. Litecoin became one of the most well-liked Bitcoin substitutes by 2012, after garnering a devoted fan base.
In 2013, a new strategy was used by Ripple (XRP). In contrast to Bitcoin and Litecoin, Ripple served as both a cryptocurrency and a digital payment technology designed to make low-cost, instantaneous international money transactions possible. Differentiating itself from other cryptocurrencies, Ripple focused on collaborating with financial institutions, and by 2014, it had forged alliances with multiple big banks.
The launch of Ethereum by Vitalik Buterin in 2014 marked yet another significant turning point in the development of alternative cryptocurrencies. Ethereum’s development and the idea of smart contracts were extensively discussed in 2014, even though the platform was officially introduced in 2015. Ethereum changed the game by enabling programmers to create decentralized apps (DApps) on its network that run on Ether (ETH), the platform’s native coin.
This breakthrough made it possible for blockchain to be used for purposes other than straightforward transactions, such as non-fungible tokens (NFTs), decentralized finance (DeFi), and more.
Many more altcoins were developed at this time, all of them exploring with various features, consensus techniques, and use cases. Some, like Dash and Monero, concentrated on anonymity, while others sought to increase scalability or provide more user-friendly platforms. The cryptocurrency market’s diversification was a sign of the public’s rising interest in blockchain technology and their conviction that its potential applications extend beyond the initial goals of Bitcoin.

The Rise of DeFi and NFTs (2020-2022)
The emergence of Decentralized Finance (DeFi) and Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) between 2020 and 2022 marked a revolutionary leap for blockchain technology. These developments changed the digital economy in addition to extending the uses of blockchain technology.
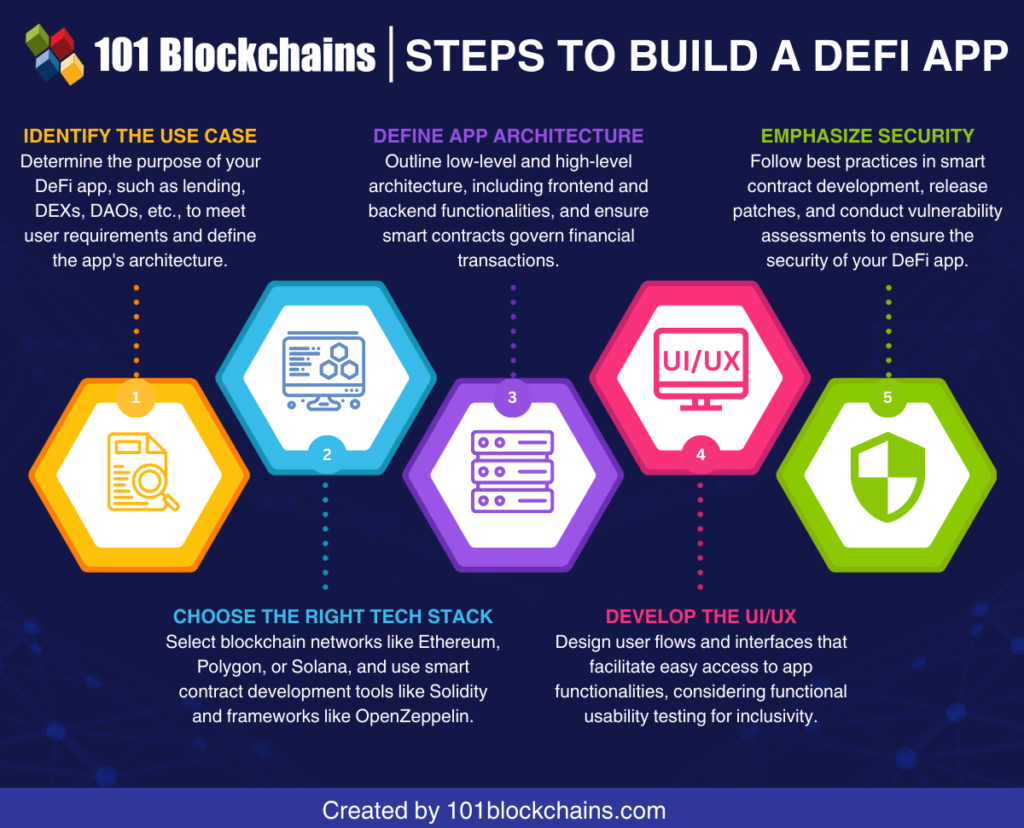
In the blockchain arena, Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has become a revolutionary force. DeFi runs on blockchain networks, namely Ethereum, in contrast to traditional finance, which is dependent on centralized organizations like banks. Through smart contracts, it seeks to replicate and improve financial services including lending, borrowing, and trading. Decentralization lowers expenses, gets rid of middlemen, and improves accessibility. By 2020, DeFi was being led by platforms like Uniswap and Compound, which let users trade assets, earn interest, and get financial services without being restricted by traditional banking practices. In DeFi protocols, the total value locked (TVL) increased.
The Future of Blockchain Trends Beyond 2024
Looking ahead to 2024, a number of significant themes that promise to further transform the digital landscape will continue to affect the direction of blockchain technology. The potential of blockchain technology is only going to grow as a result of technological developments and growing industry acceptance.
1.Web3 and Decentralized Applications (DApps) Expansion: The goal of Web3, the upcoming version of the internet, is to establish a decentralized web in which people have more control over their digital interactions and data. This shift is primarily driven by blockchain technology, which makes it possible for decentralized applications (DApps) to function without the need for central authority. Increased security, transparency, and user autonomy are all promised by these applications.
2: integration with the Metaverse: Blockchain technology will be used more and more in the metaverse, a collective virtual shared place that is produced by the fusion of virtually improved physical reality and physically persistent virtual reality. The infrastructure that blockchain will provide for in-game economies, virtual real estate, and digital ownership will guarantee the security, traceability, and decentralization of all assets and transactions.
- Enhanced Security and Privacy Solutions: As blockchain technology develops, strengthening security and privacy will become increasingly important. Technological developments in cryptography, such zero-knowledge proofs, will make transactions more transparent and safe while preserving privacy. These upgrades will take care of some of the present issues and restrictions around the application of blockchain technology.
- Interoperability Across Blockchains: Interoperability, which enables smooth communication and interaction between various blockchain networks, will receive more attention in the future of blockchain technology. This will make it possible to integrate different blockchain systems, increasing their usefulness and functionality. Cross-chain interaction-facilitating platforms and protocols will be essential to this evolution.
- Adoption in Conventional businesses: Blockchain is anticipated to acquire additional momentum in conventional businesses including supply chain management, healthcare, and legal services, in addition to finance and technology. Efficiency, traceability, and trust in these industries will all increase because to blockchain’s capacity to provide clear, unchangeable records.
- Regulation and Compliance: In order to handle the intricacies of blockchain technology, regulatory frameworks will change as it becomes more widely used in the economy. It is probable that forthcoming advancements would encompass more precise protocols and benchmarks to guarantee adherence while promoting creativity.
- Environmental and Scalability Solutions: A major emphasis will be on addressing the environmental impact of blockchain technology, especially in relation to energy-intensive proof-of-work systems. Blockchain technology will grow more energy-efficient and scalable as innovations like proof-of-stake and other consensus methods proliferate.
…
Conclusion of blockchain
Since the introduction of blockchain technology with Bitcoin in 2008, the technology has advanced significantly to its current state and beyond. Blockchain’s journey has been characterized by the emergence of rival cryptocurrencies, the revolutionary influence of Ethereum’s smart contracts, and the explosive growth of DeFi and NFTs, beginning with the ground-breaking debut of Bitcoin.

